China-Japan Rare Earth Fracas Continues
posted on
Oct 18, 2010 08:16AM

Edit this title from the Fast Facts Section

http://seekingalpha.com/article/230426-china-japan-rare-earth-fracas-continues?source=dashboard_macro-view
Despite earlier news reports that it had come to an end, China’s unofficial embargo on rare earth exports to Japan (which I reported on in a prior post) now appears to be continuing into its fourth week. This rather surprising development gives rise to a couple of thoughts: So the question remains: precisely what game are China’s leaders playing at here, and how far are they willing to take it?
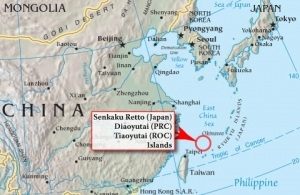 What objective is China pursuing, and who exactly is driving the agenda? The immediate diplomatic flare-up that sparked China’s action has been long since put to bed (both countries have returned each other’s detained citizens), although the underlying territorial dispute over the Senkaku/Diaoyutai Islands remains unresolved. The only logical explanation for continuing the embargo is that China wants to demonstrate its capacity to “punish” Japan in order to gain future leverage in the dispute. Of course, it also runs the risk of alerting Japan and other potential rivals (including the U.S.) of the risks inherent in China’s virtual monopoly over rare earth production, and provoking efforts to open up alternative sources of supply. It’s also unclear whether China’s assertive stance represents a consensus among Chinese leaders, or whether certain elements (like the PLA) are driving policy, while others (such as the Commerce and Foreign ministries) are merely along for the ride. There has been some speculation that China’s upcoming leadership transition, in 2013, offers a prime opportunity for the PLA to flex its political muscles.
What objective is China pursuing, and who exactly is driving the agenda? The immediate diplomatic flare-up that sparked China’s action has been long since put to bed (both countries have returned each other’s detained citizens), although the underlying territorial dispute over the Senkaku/Diaoyutai Islands remains unresolved. The only logical explanation for continuing the embargo is that China wants to demonstrate its capacity to “punish” Japan in order to gain future leverage in the dispute. Of course, it also runs the risk of alerting Japan and other potential rivals (including the U.S.) of the risks inherent in China’s virtual monopoly over rare earth production, and provoking efforts to open up alternative sources of supply. It’s also unclear whether China’s assertive stance represents a consensus among Chinese leaders, or whether certain elements (like the PLA) are driving policy, while others (such as the Commerce and Foreign ministries) are merely along for the ride. There has been some speculation that China’s upcoming leadership transition, in 2013, offers a prime opportunity for the PLA to flex its political muscles. In the meantime, yesterday (Saturday) saw some large anti-Japanese street protests in several Chinese cities. According to the Associated Press,thousands of studentsmarched in Xi’an, Chengdu, and Zhengzhou. The accompanying photos from Xi’an were emailed to me, and give some sense of the size and vehemence of the rallies (pardon the language, but it gets the point across clearly enough). Hong Kong’s Apple Daily puts the overall number of participants at 50,000, and adds Hangzhou to the list. It also reports that several students said the protests had been organized by official (state-sponsored) student organizations at their universities.
In the meantime, yesterday (Saturday) saw some large anti-Japanese street protests in several Chinese cities. According to the Associated Press,thousands of studentsmarched in Xi’an, Chengdu, and Zhengzhou. The accompanying photos from Xi’an were emailed to me, and give some sense of the size and vehemence of the rallies (pardon the language, but it gets the point across clearly enough). Hong Kong’s Apple Daily puts the overall number of participants at 50,000, and adds Hangzhou to the list. It also reports that several students said the protests had been organized by official (state-sponsored) student organizations at their universities. Although China’s Xinhua news agency issued a report in English, AP said the protests had not been covered by the Chinese-language state media, and local police refused to acknowledge they had taken place. Chinese authorites tend to be pretty cagey about mass protests, even on “safe” state-sanctioned issues, using them to make a point, then sharply reining them in if they threaten to take on their own momentum.
Although China’s Xinhua news agency issued a report in English, AP said the protests had not been covered by the Chinese-language state media, and local police refused to acknowledge they had taken place. Chinese authorites tend to be pretty cagey about mass protests, even on “safe” state-sanctioned issues, using them to make a point, then sharply reining them in if they threaten to take on their own momentum.